Aug . 07, 2024 14:25 Back to list
High-Quality Galvanized Iron Wire Production for Durable Fencing Solutions and Agricultural Applications
The Importance of Galvanized Iron Wire in Fencing Insights from a Modern Factory
In the ever-evolving world of construction and agriculture, the importance of robust fencing solutions cannot be underestimated. One of the materials gaining prominence in this field is galvanized iron wire. This article will delve into the advantages of using galvanized iron wire for fencing, while also taking a closer look at the manufacturing processes within a modern factory producing this essential material.
Understanding Galvanized Iron Wire
Galvanized iron wire is produced by coating iron with a layer of zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. This protective layer prevents rust and deterioration, which is particularly important in outdoor applications such as fencing. The process of galvanization not only extends the lifespan of the wire but also makes it ideal for various environmental conditions, including moisture, extreme temperatures, and exposure to chemicals.
Applications of Galvanized Iron Wire
The applications of galvanized iron wire are diverse. In agricultural settings, it is commonly used to build fences that secure livestock and protect crops from wildlife. In urban environments, it serves as a barrier for construction sites and private properties. Furthermore, its use extends to sporting facilities, where it is employed in the construction of basketball courts, tennis courts, and other recreational areas, ensuring safety without compromising visibility.
Manufacturing Process in a Factory
The manufacturing of galvanized iron wire involves several critical steps to ensure that the final product meets industry standards.
galvanized iron wire for fencing factory
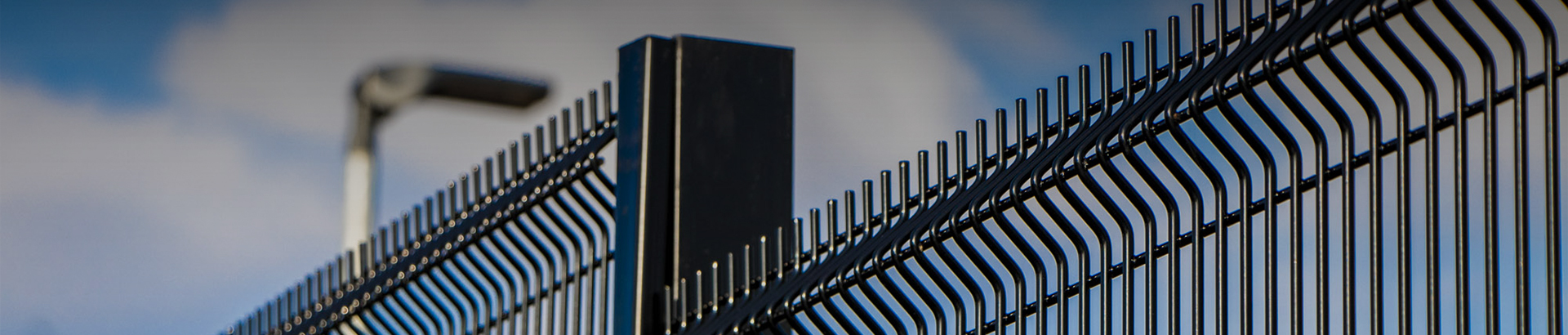
1. Wire Drawing The process begins with wire drawing, where raw materials, often iron rods, are pulled through a series of dies to achieve the desired thickness. This step is crucial as the diameter of the wire directly affects strength and application suitability.
2. Cleaning After drawing, the wires undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove any oxides, oils, or other contaminants that could affect the quality of the galvanization. This is typically done using acid or caustic solutions followed by rinsing.
3. Galvanization The cleaned wires are then subjected to the galvanization process. This is commonly achieved through hot-dip galvanization, where the wire is submerged in molten zinc. This rapid coating method ensures a strong bond between the zinc and the iron, providing long-lasting corrosion resistance.
4. Cooling and Drying After galvanization, the wire needs to cool and dry. Cooling time is essential to ensure that the zinc layer solidifies well and adheres uniformly to the wire.
5. Quality Control Before the finished products leave the factory, they undergo stringent quality control measures. Tests for tensile strength, elongation, and rust resistance ensure that only the best quality galvanized iron wire reaches the market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, galvanized iron wire is an indispensable material in the fencing industry, known for its durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Through advanced manufacturing processes in modern factories, this wire is produced to high standards, meeting the demands of various sectors. As the need for secure and reliable fencing solutions continues to grow, galvanized iron wire will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of material choices for both industrial and agricultural applications. Whether protecting livestock, securing properties, or enclosing recreational areas, galvanized iron wire stands as a testament to resilient engineering and smart design.
-
Welded Wire Mesh for Industry Factory - Anping County Puersen Hardware Wire Mesh Products Co., Ltd.
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Welded Wire Mesh for Industry Factory | Durable & Cost-Effective Solutions
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Durable Welded Wire Mesh for Industry Factory | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Durable Welded Wire Mesh for Industry Factory - High Quality
NewsAug.26,2025
-
Leading Galvanized Steel Fence Factory | Durable & Secure Fencing
NewsAug.24,2025
-
Welded Wire Mesh for Industry Factory - Durable & Custom Solutions
NewsAug.23,2025

